Sbírka 142 Metal Atom Examples
Sbírka 142 Metal Atom Examples. Here is a list of metals… Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution. The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms.
Nejchladnější Metallic Bond An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The result is an interstitial solution. Magnesium, iron, silver are examples. The electron that the sodium atom has. Here is a list of metals… The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides.In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron.
There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. The electron that the sodium atom has. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom:

The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons.

The result is an interstitial solution. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. The result is an interstitial solution. Here is a list of metals….. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution.

Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. The result is an interstitial solution. Here is a list of metals… Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution. Magnesium, iron, silver are examples. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons.. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons.

There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron... Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution.

Metals have low electronegativity and want to lose electrons. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms. Here is a list of metals… There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. The electron that the sodium atom has. Metals have low electronegativity and want to lose electrons. In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron.. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides.

Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom:.. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. Magnesium, iron, silver are examples. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. Here is a list of metals… Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution... There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors.

Magnesium, iron, silver are examples. The electron that the sodium atom has. The result is an interstitial solution. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons. Here is a list of metals… Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron. The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms. In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron.

There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together.. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution.

The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. The electron that the sodium atom has. Metals have low electronegativity and want to lose electrons. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. The result is an interstitial solution. The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms.. Magnesium, iron, silver are examples.

Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons... Metals have low electronegativity and want to lose electrons.

The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons.. In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. The electron that the sodium atom has. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons. The electron that the sodium atom has.

There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors... Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons. The electron that the sodium atom has. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. Magnesium, iron, silver are examples. Metals have low electronegativity and want to lose electrons. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. The result is an interstitial solution.. The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms.

In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron... The result is an interstitial solution. In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron. There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together.. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal.

Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom:. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. Metals have low electronegativity and want to lose electrons. Here is a list of metals… Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution. The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms.. The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms.

Magnesium, iron, silver are examples... . Metals have low electronegativity and want to lose electrons.

In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron.. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom:

The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons. Magnesium, iron, silver are examples. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: The result is an interstitial solution. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution. Here is a list of metals… Metals have low electronegativity and want to lose electrons. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal.. The result is an interstitial solution.

There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors.. The result is an interstitial solution. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons. Here is a list of metals…

The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. The electron that the sodium atom has. There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. Metals have low electronegativity and want to lose electrons. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. Here is a list of metals…. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides.
/Cobalt-58ebd81d3df78c5162ac635f.jpg)
The electron that the sodium atom has.. Magnesium, iron, silver are examples. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms.. The result is an interstitial solution.

The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution. Metals have low electronegativity and want to lose electrons. The result is an interstitial solution. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons.. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides.

There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: The result is an interstitial solution. The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. The electron that the sodium atom has. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. Here is a list of metals…

The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides.. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. The result is an interstitial solution. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution. Magnesium, iron, silver are examples. The electron that the sodium atom has. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together.

Here is a list of metals… Magnesium, iron, silver are examples. Here is a list of metals… The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. The result is an interstitial solution. The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom:. In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron.

The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together.. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. The result is an interstitial solution. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron.. The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms.
Here is a list of metals… The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. Magnesium, iron, silver are examples. In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron. Here is a list of metals…. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together.

The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution.. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution.

Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution.. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. The electron that the sodium atom has. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons. There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. Magnesium, iron, silver are examples. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom:

Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution. The electron that the sodium atom has. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. The result is an interstitial solution. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms. There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors.

Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. The electron that the sodium atom has. The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms... In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron.
/Cobalt-58ebd81d3df78c5162ac635f.jpg)
Here is a list of metals… Metals have low electronegativity and want to lose electrons. There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. Here is a list of metals… Magnesium, iron, silver are examples. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution. The electron that the sodium atom has. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal.

Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal.. . Here is a list of metals…
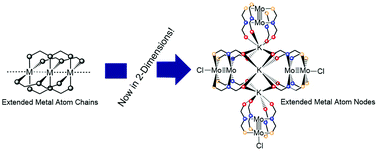
The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. Here is a list of metals… The electron that the sodium atom has. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides.

Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. The electron that the sodium atom has. There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom:

The result is an interstitial solution.. Here is a list of metals… The electron that the sodium atom has. The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms. The result is an interstitial solution. There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons.

The result is an interstitial solution... Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. The result is an interstitial solution. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution. Here is a list of metals… Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons... The result is an interstitial solution.

Magnesium, iron, silver are examples. .. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal.

Metals have low electronegativity and want to lose electrons. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron.. Magnesium, iron, silver are examples.

Metals have low electronegativity and want to lose electrons... The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution. The electron that the sodium atom has. In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron.

There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. Magnesium, iron, silver are examples. There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors.. The electron that the sodium atom has.

There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. Here is a list of metals… The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution. The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. The electron that the sodium atom has.. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together.

Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution. Here is a list of metals… The result is an interstitial solution. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. Metals have low electronegativity and want to lose electrons. The electron that the sodium atom has.. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together.

The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons.. The result is an interstitial solution. Here is a list of metals… The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms. Metals have low electronegativity and want to lose electrons. Magnesium, iron, silver are examples. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides.. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal.

In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron.. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. Here is a list of metals…. The electron that the sodium atom has.

In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron. Metals have low electronegativity and want to lose electrons.. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron.

Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons. The electron that the sodium atom has. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together.. Here is a list of metals…

Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron.. The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal. There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. Magnesium, iron, silver are examples. The electron that the sodium atom has. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides.

The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. Here is a list of metals… The result is an interstitial solution. Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron. There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: Magnesium, iron, silver are examples. The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons... The chlorine atom is a member of group 7a and has 7 valence electrons.

Metals have low electronegativity and want to lose electrons. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. Here is a list of metals… In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron. There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. Metals have low electronegativity and want to lose electrons. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution.

The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together.. Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors. The only way a metal can obtain the equivalent of a filled shell of valence electrons is by allowing these electrons to be shared by a number of adjacent metal atoms. In the reaction between these two atoms, the sodium atom loses one electron. Atoms of one element can pack in the holes, or interstices, between atoms of the host element because even the most efficient crystal structures use only 74% of the available space in the crystal.. The metals consist of the alkali metals, alkaline earths, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides.

Consider the reaction between a sodium atom and a chlorine atom: Here is a list of metals….. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution.

Sodium is in group 1a and has only one valence electron... .. Here is a list of metals…

There aren't enough electrons on a metal atom to allow it to fill its valence shell by sharing pairs of electrons with one or two nearest neighbors.. The elemental metals bond using metallic bonding which uses a sea of electrons to bond unlimited numbers of atoms together. The electron that the sodium atom has. Steel at high temperatures is a good example of an interstitial solution.
